Supply Chain Attacks: The Growing Threat and Mitigation Strategies
Photo by Adi Goldstein on Unsplash
The intricate web of interconnected businesses, known as the supply chain, has become an increasingly attractive target for cybercriminals. Supply chain attacks, where malicious actors infiltrate an organization by compromising its suppliers or vendors, pose a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. This blog delves into the nature of these attacks, their devastating consequences, and the essential steps organizations can take to protect themselves.
Understanding Supply Chain Attacks
A supply chain attack occurs when adversaries target a weaker link in an organization’s supply chain to gain unauthorized access to its systems or data. These attacks can range from stealing intellectual property to disrupting operations, causing financial loss, and damaging brand reputation.
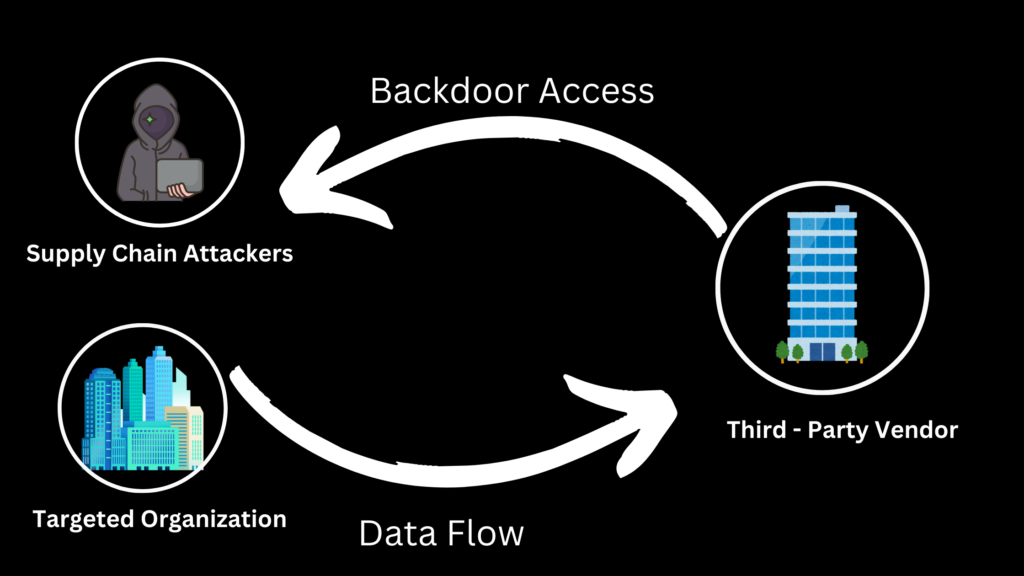
Common attack vectors include:
- Software supply chain attacks: Malicious code is introduced into software updates or third-party components.
- Hardware supply chain attacks: Counterfeit or tampered hardware components are inserted into the supply chain.
- Email and phishing attacks: Employees are targeted with phishing emails to gain access to systems.
- Insider threats: Malicious actors within the organization exploit their access to compromise the supply chain.
The Growing Threat Landscape
The sophistication and frequency of supply chain attacks have surged in recent years. Several high-profile incidents, such as the SolarWinds hack, have highlighted the devastating impact these attacks can have.
Factors contributing to the growing threat include:
- Increased complexity: Modern supply chains are increasingly global and interconnected, making them more difficult to secure.
- Digital transformation: The shift towards digital operations has expanded the attack surface.
- Economic espionage: Cybercriminals are motivated by financial gain and intellectual property theft.
- Nation-state involvement: State-sponsored actors are increasingly targeting critical infrastructure and supply chains.
The Impact of Supply Chain Attacks
The consequences of a supply chain attack can be far-reaching and catastrophic. Organizations may face:
- Financial losses: Direct costs of the attack, including ransom payments, legal fees, and business interruption.
- Reputation damage: Loss of customer trust and confidence.
- Legal and regulatory liabilities: Compliance breaches and potential lawsuits.
- Supply chain disruptions: Interruptions in production, distribution, and customer service.
- Intellectual property theft: Loss of valuable trade secrets and competitive advantage.
Protecting Your Organization
To mitigate the risk of supply chain attacks, organizations must adopt a comprehensive and proactive approach:
Vendor Risk Management
- Due diligence: Conduct thorough assessments of potential and existing suppliers to evaluate their security posture.
- Continuous monitoring: Monitor supplier performance and security practices on an ongoing basis.
- Incident response planning: Develop joint incident response plans with critical suppliers.
Cybersecurity Best Practices
- Employee training: Educate employees about the risks of supply chain attacks and how to identify and report suspicious activities.
- Strong password policies: Enforce the use of complex passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Regular software updates: Keep operating systems and applications patched to address vulnerabilities.
- Data encryption: Protect sensitive data with robust encryption.
- Network segmentation: Isolate critical systems and data to limit the impact of a breach.
Supply Chain Visibility
- Supply chain mapping: Identify and understand all components of the supply chain.
- Risk assessment: Evaluate the potential risks associated with each supplier.
- Third-party risk management tools: Utilize specialized software to assess and monitor supplier security.
Incident Response and Recovery
- Incident response plan: Develop a comprehensive plan to address supply chain attacks.
- Cybersecurity insurance: Consider purchasing insurance to mitigate financial losses.
- Business continuity planning: Ensure the organization can continue operations in the event of a disruption.
Emerging Technologies
- Artificial intelligence: Leverage AI-powered tools for threat detection and response.
- Blockchain: Explore the potential of blockchain for supply chain transparency and security.
Conclusion
Supply chain attacks represent a complex and evolving threat that demands a multifaceted approach to mitigation. By prioritizing vendor risk management, implementing robust cybersecurity measures, and fostering strong relationships with suppliers, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to these attacks. Continuous vigilance, adaptation, and collaboration are essential to staying ahead of the evolving threat landscape.
Additional Considerations:
- Industry-specific regulations: Adhere to relevant industry standards and regulations to protect sensitive data.
- Third-party audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to verify compliance with security standards.
- Cybersecurity awareness: Foster a culture of security within the organization.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can build a resilient supply chain capable of withstanding the challenges posed by cyber threats.
Here Is A Video Of Me Explaing the topic






